Database Design
Table Design
Based on the functional and non-functional requirements outlined in the previous section - Software Requirement, the team decided to build a database focused on scalability, capable of being divided into parts to serve specific roles, and suitable for applying a microservices architecture.
The database schema will be adjusted to focus on e-commerce in the fashion industry.
Additionally, to meet the data needs for AI services applied to the system for efficient operation, the schema needs to be designed to allow the execution of queries for statistical information on a very large dataset, either as time series or general statistics, quickly and accurately. Furthermore, the database schema must be designed to be easily customizable without affecting other components, fitting the context of frequent schema updates during the development of Vagoda.
List of significant tables
- Accounts: Stores and manages user account information.
- Cart: Stores and manages information about customer shopping cart.
- Categories: Stores and manages information about predefined general categories.
- CollectionTypes: Stores and manages information about store collections.
- Comments: Stores and manages information about comments on any product reviews
- Files: Stores and manages information about files used for bulk product creation.
- Orders: Stores and manages information about orders.
- ProductAccesses: Stores and manages information about accessed products.
- Products: Stores and manages information about products.
- Promotions: Stores and manages information about discount codes
- RefreshTokens: Stores and manages records of issued refresh tokens.
- Reviews: Stores and manages information about customer reviews of any products.
- Shops: Stores and manages information about shops.
- SubCategories: Stores and manages information about predefined subcategories.
- SubCategoriesTypes: Stores and manages information about product types within predefined subcategories.
- Users: Stores and manages information about buyers
- Widgets: Stores and manages predefined widgets for seller to customize their interface.
ER Diagram describes relationships of tables in the database
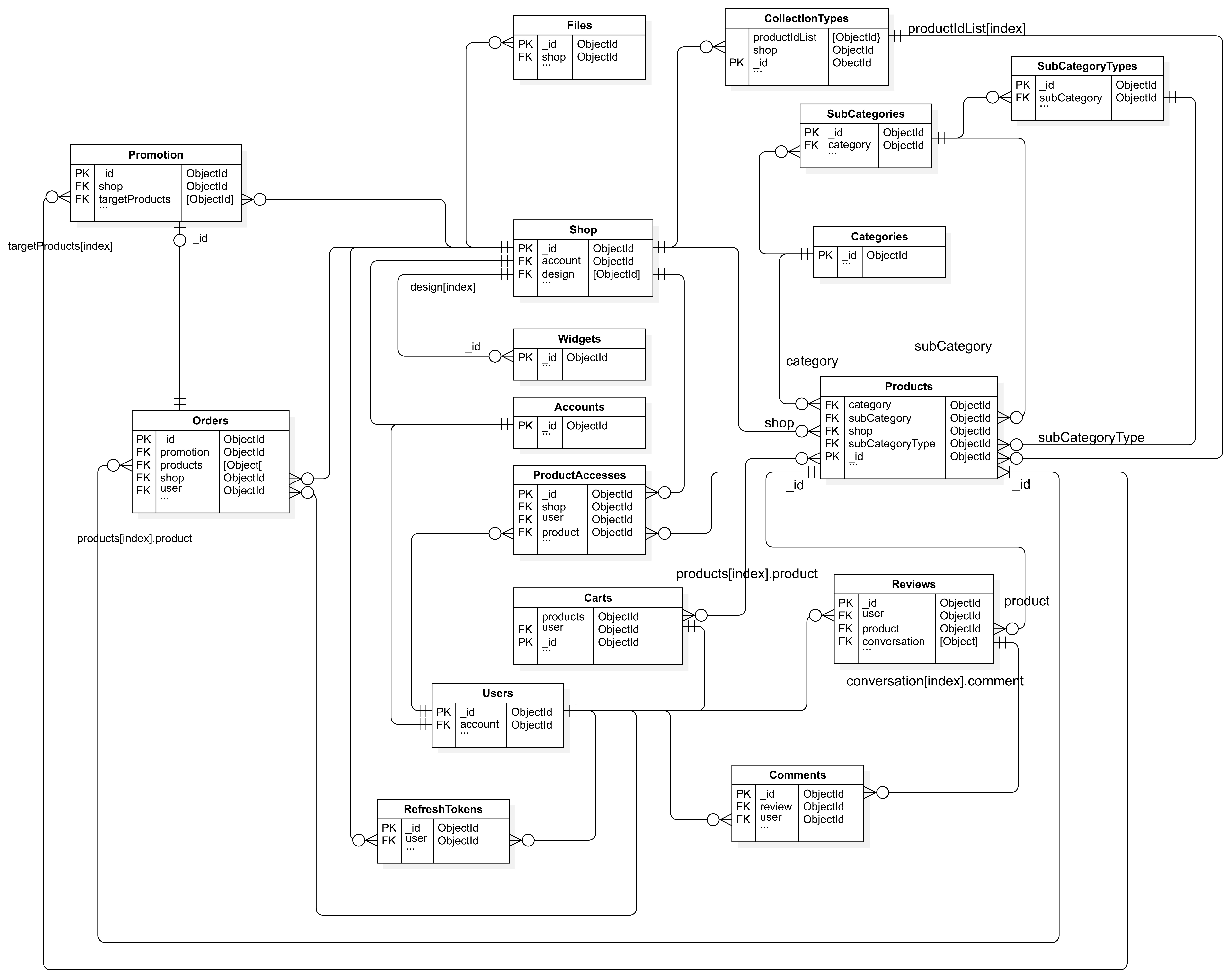
ER Diagram of the database
To illustrate the relationships between the sets, the sets are depicted on a diagram with reduced data fields, retaining only the reference fields. The diagram describes the reference relationships between values in the sets.
However, when implemented in a microservices architecture, these references will be theoretical, as the sets may not reside on the same data server. Instead, the general database will be divided into distributed databases across multiple servers, with each server (service) assuming a specific role in an e-commerce system using a microservices architecture.
Detail of significant tables
Some conventions
- PK - primary key: used to identify a record in a table, and be unique for each value.
- FK - foreign key: represents the reference of its value to other tables.
- U - unique: describes a field or an object containing a unique value for each record.
Detail descriptions
The below descriptions is details of the structure and fields of some tables.
- Accounts
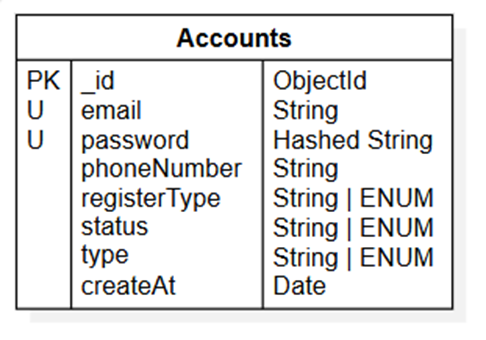
Structure of Accounts table
- Orders
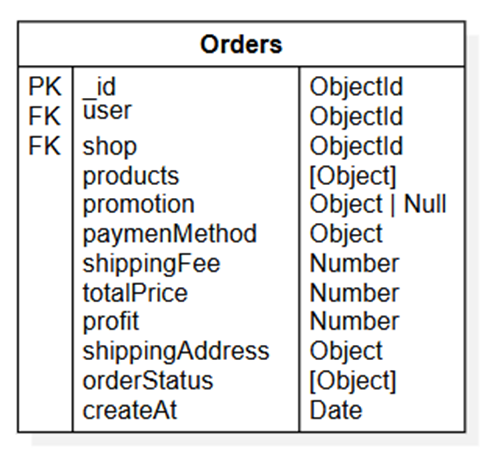
Structure of Orders table
- Products
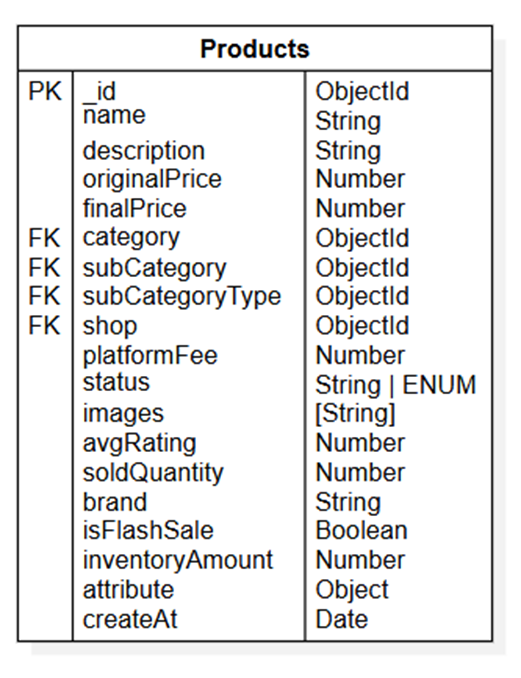
Structure of Products table
- Promotions
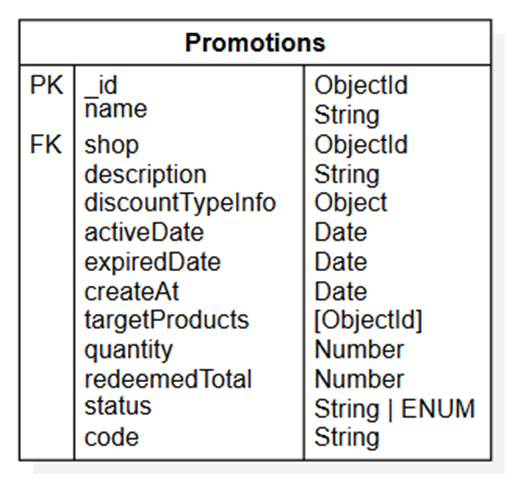
Structure of Promotions table
- Reviews
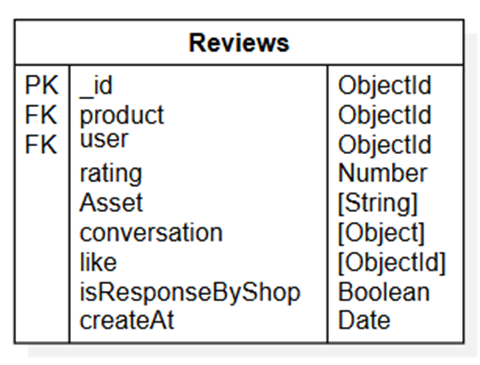
Structure of Reviews table
Data Flow
This section presents the data flows when the system is in operation. The document explains how data is generated and modified as users interact with the Vagoda system, how data is stored, and how it is used within the system. The document provides readers with a detailed and visual understanding of the operational flow of the database system in particular and the e-commerce platform in general.
Some symbols and conventions
- External Entity

- Process
- Data Store
- Data Flow

Essential Data Flows
Level 0
First, at a general level, the document will present the Data Flow at level 0.
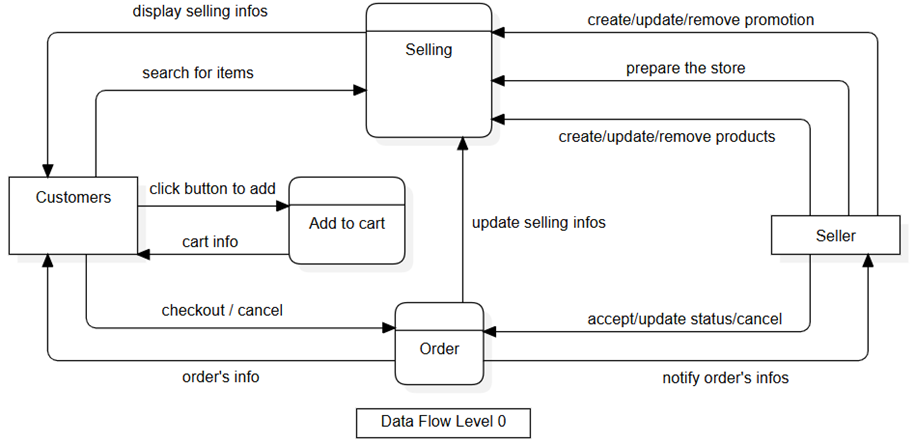
General Data Flow - Level 0
At level 0, the diagram illustrates the core processes of an e-commerce system, which is the buying and selling process between customers and sellers.
Customers visit the website to search for the products they need, with the storefront interface displaying product information and promotions prepared by the sellers. Customers place orders, perform actions related to updating order statuses, and the system sends requests to the sellers. Information about purchase history or statistics regarding the store, customers, and products helps sellers adjust their storefront, product offerings, and current promotions to increase revenue.
Level 1
At level 1, the document presents the Data Flows in the main processes occurring within the system.
Add-to-cart flow
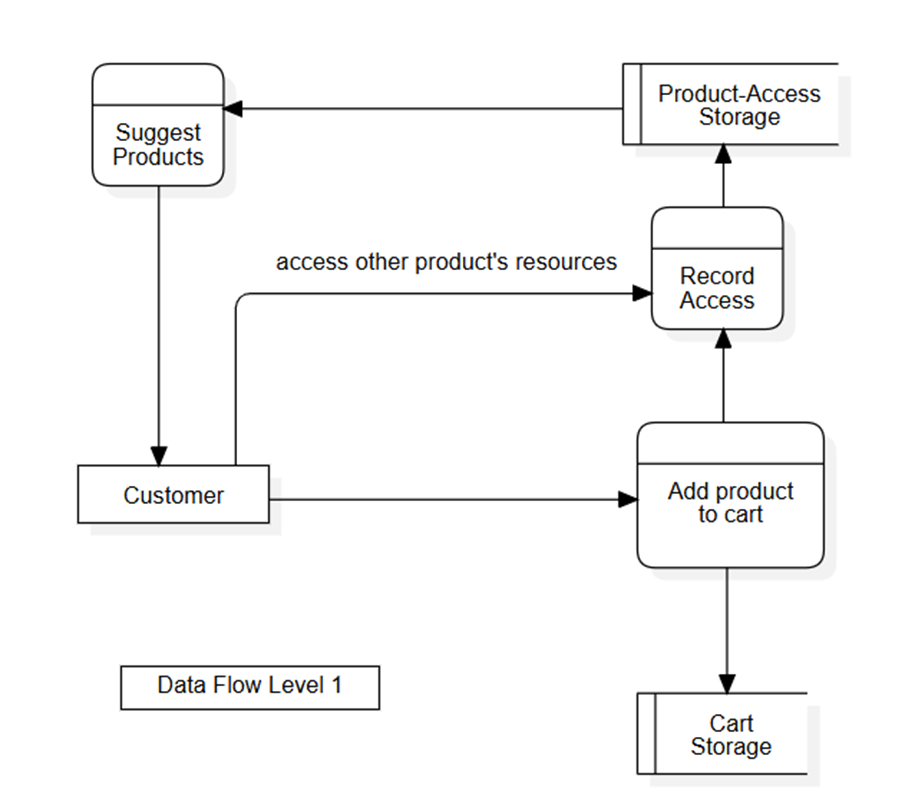
Data Flow Level 1 - Add-to-cart process
The data flow described outlines the event when a customer adds a product to their cart.
When executing this process, the system retrieves data from the product database, extracts the necessary information fields, and then stores and manages this data in a collection called Cart Storage. This ensures that the customer's cart data is always maintained under any conditions. In addition to cart storage, the system also records customer product accesses in Product-Access Storage. This allows for the evaluation of user behavior and provides personalized purchase recommendations for each customer.
Update-selling-information flow
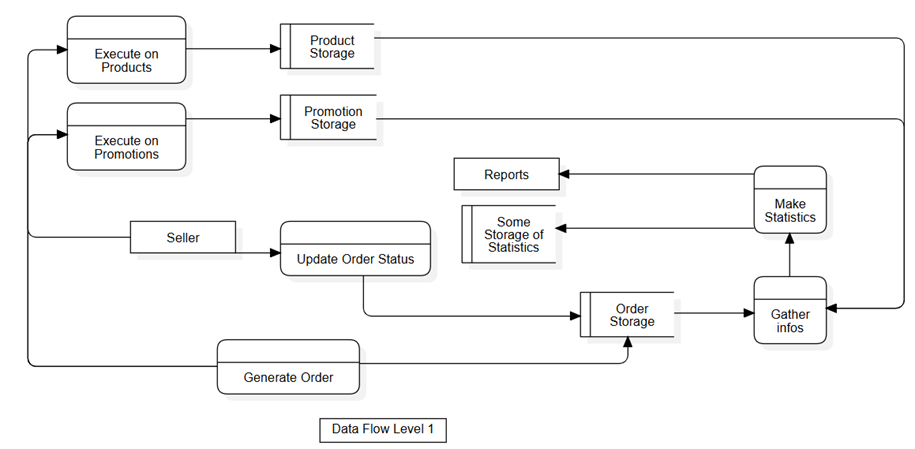
Data Flow Level 1 - Update-selling-info flow
From the seller's perspective, they can make changes related to product information and store discount codes.
These changes are recorded and managed in Product Storage and Promotion Storage, respectively. Creating and updating order status information, such as order confirmation or cancellation, is recorded in Order Storage. Information related to products and discount codes, like inventory levels and sales quantities, is updated by the system (the flow executes from Generate Order to Execute on Products and Execute on Promotions).
Storing detailed information about sales activities allows the system to collect data and perform statistics on sales, revenue, the number of products sold, etc., to generate reports that help sellers monitor and adjust their business as needed. Additionally, some statistical information is recorded by the system for long-term support tasks and future scalability.
Register an account
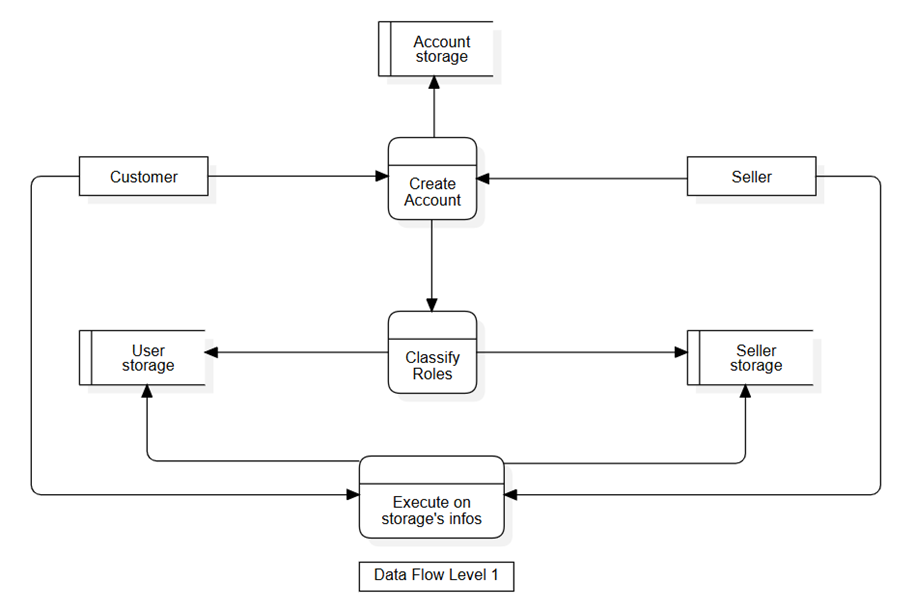
Data Flow Level 1 - Register-an-account flow
When users submit a request to create an account, the system performs several processes including user account creation, user classification, and creating a record of user information in a designated collection.
Account information is stored and managed in Account Storage and does not include personal information about the account holder. For user account information, there are two main classifications: buyers and sellers. The system classifies users based on the role specified in the provided data and determines the collection used to record user information.
- For buyers, the system records and manages personal information in User Storage.
- For sellers, the system records and manages personal information in Seller Storage.
Separating the storage collections for user accounts and user information offers several benefits, such as:
- Supporting maintenance and development by clearly distinguishing different types of data by function and structure.
- Sensitive information about authentication and authorization is managed separately in a distinct collection with independent methods, unaffected by business operations.
- Supporting independent scalability as the dataset grows. Additionally, the separation supports role-based storage, allowing for the flexible expansion of user information storage with different roles and data fields while still using the existing account management system.
Execute on order request
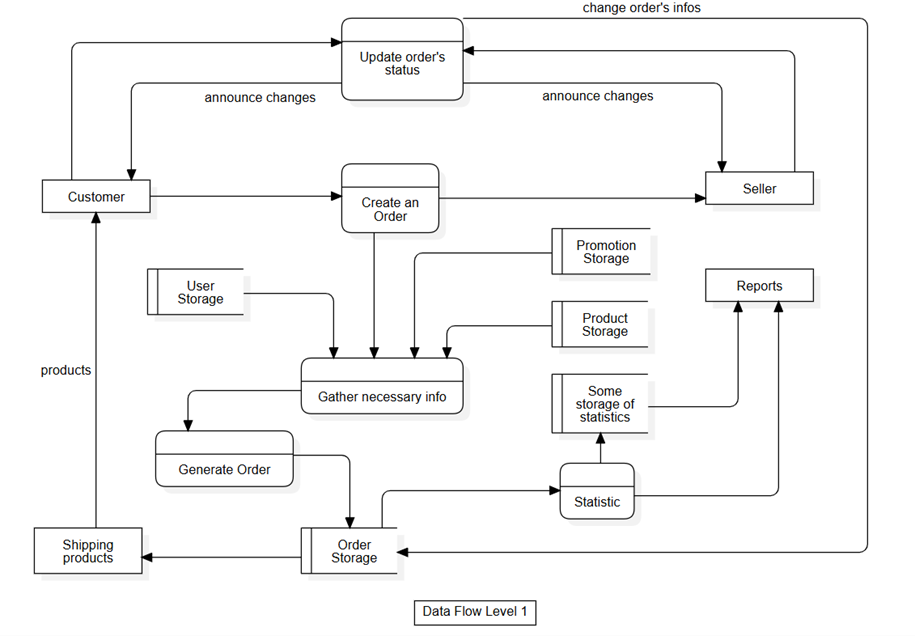
Data Flow Level 1 - Execute on order process
The data flow describes how an order is created and the subsequent changes in the dataset when the order status is updated.
When a customer submits a request to create an order, the system collects necessary information such as user details, shipping address, ordered product information, and any applied discount codes to create a complete record. This record is stored in the Order Storage collection, and the seller is also notified and can access this information.
When the order status is updated by either the customer (e.g., order cancellation) or the seller (e.g., order confirmation or cancellation), the system executes changes on the Order Storage collection. The information in the records on Order Storage serves as the basis for the seller to prepare and ship orders to the customer. Additionally, order information helps the system perform statistics and generate reports to support the seller in monitoring and managing the store’s business, and it aids AI services in operating efficiently.