System Architecture Design
Design Objectives
-
Scalability: The e-commerce system must be scalable to serve an increasing number of users and meet growing business demands. Using microservices architecture allows for easy scalability by adding new services or expanding existing ones without impacting the entire system.
-
Maintainability: Microservices architecture enables independent development, deployment, and maintenance of services. This makes it easier for the development team to update, fix bugs, and upgrade individual parts of the system without disrupting the operations of other parts.
-
High Performance: Breaking down functionalities into smaller services optimizes system performance. Each service can be deployed and scaled independently, optimizing resource usage and reducing user response times.
System Architecture Overview
-
General Architecture Model: The system uses a microservices architecture, where each service handles a specific function. Services communicate via APIs and are managed by an API Gateway, facilitating system scalability and maintainability.
-
Microservices Architecture: This approach divides the application into small, independent services. Each service performs a specific task, enabling autonomous development and deployment.
-
Clear Separation: Functions are divided into individual services, reducing complexity and improving manageability.
-
Independent Deployment: Each service can be developed and deployed independently, allowing updates without interrupting other services.
-
Technological Flexibility: Development can choose the most suitable technology for each service, optimizing performance.
Architectural Details
Architecture Layers
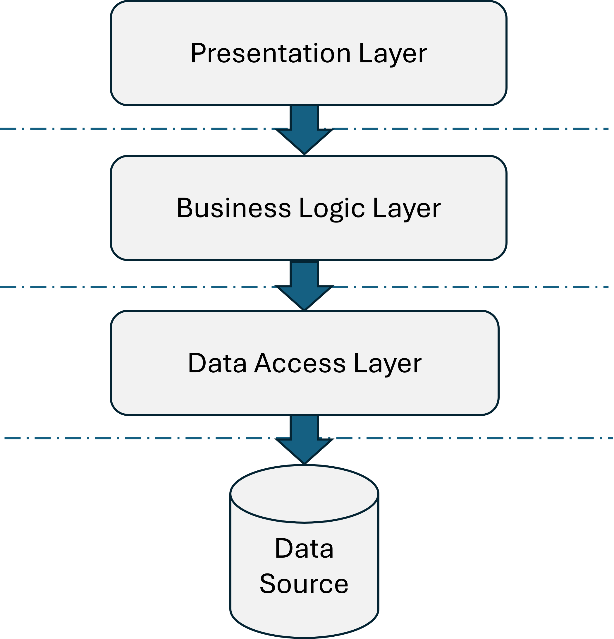
-
Presentation Layer: Responsible for the user interface, providing an intuitive and user-friendly experience.
-
Business Logic Layer: Handles business rules and logic within each service, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in data processing.
-
Data Access Layer: Manages interactions with data sources, including retrieval, storage, and efficient data management.
Key Components
-
API Gateway: Manages and routes API requests from clients.
-
AI/ML Service: Provides features related to artificial intelligence and machine learning.
-
User Service: Manages user information and profiles.
-
Payment Service: Handles payments and integrates with payment gateways.
-
Order Service: Manages orders, order statuses, and transaction histories.
-
Product Service: Manages products.
-
Auth Service: Handles user authentication and authorization.
Design Patterns
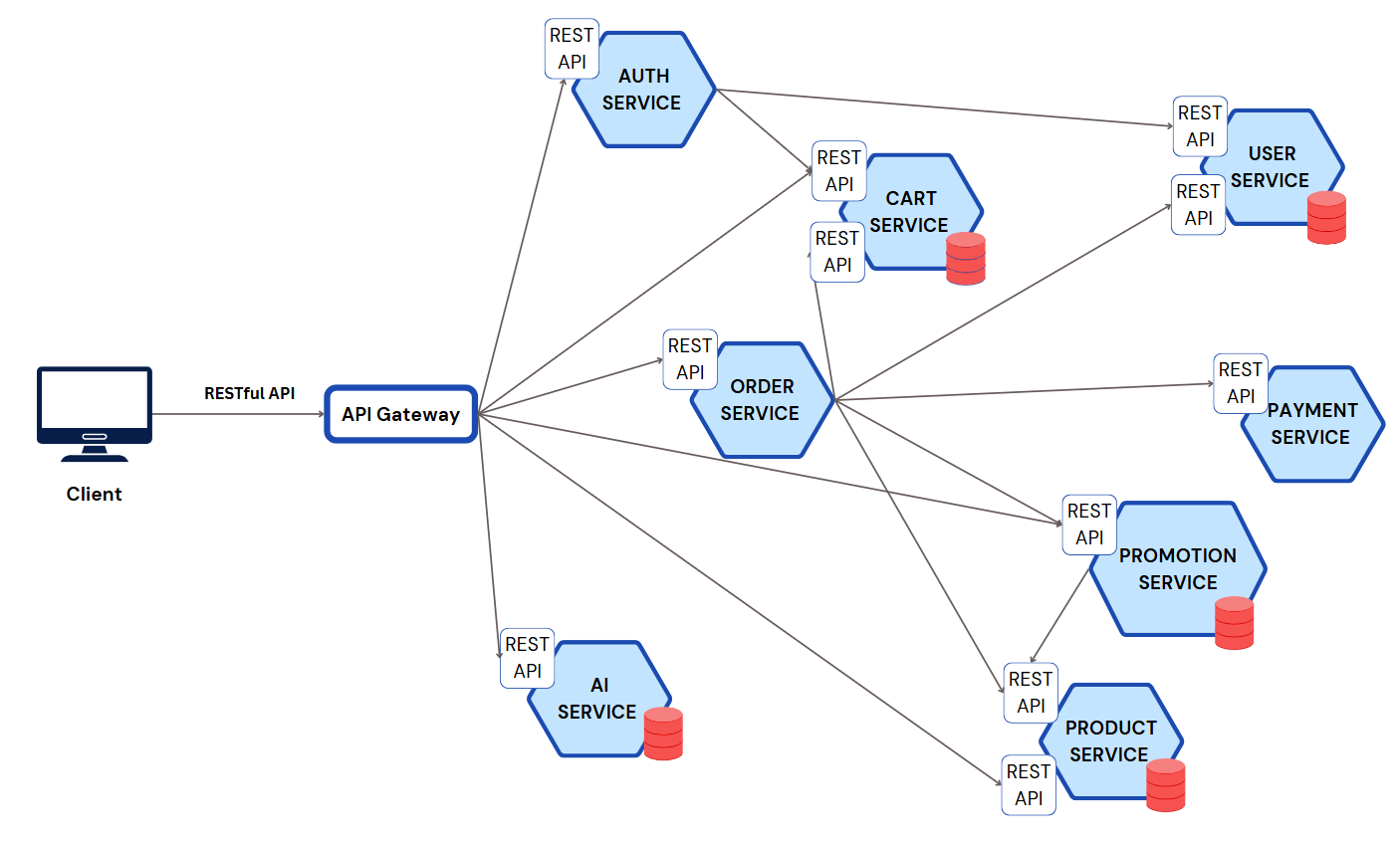
API Gateway
Manages API requests from clients and routes them to the corresponding services, providing a single entry point and optimizing traffic and security.
Design Patterns (Model-View-Controller)
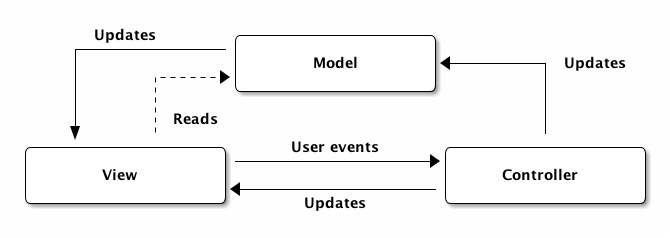
A common approach in application development, applied to organize services effectively.
-
Model: This layer interacts with the database, handling operations like creating, reading, updating, and deleting (CRUD) data. The model is responsible for data management and related business rules, ensuring data consistency and accuracy. In the context of microservices, each service can have its model to handle specific data it manages.
-
View: The View layer is responsible for displaying data to users. In this system, the View is implemented using React.js to create dynamic user interfaces. The View receives data from the backend in JSON format and displays it to the users. This separation of presentation and business logic makes the application easier to maintain.
-
Controller: The Controller layer handles the business logic of the application. It receives requests from clients, processes them by interacting with the Model, and returns results to the View. Controllers decide how data is retrieved from the Model and displayed via the View, performing business functions like user authentication, order processing, and product management.
The MVC model not only improves maintainability but also makes the application more scalable. When a component needs to change, such as updating the display (View) or modifying business logic (Controller), other components can continue to function independently. This also supports parallel development, allowing teams to work on different components without affecting each other.