Deployment and Installation Process
Agile Scrum
Agile Scrum is a flexible software development methodology that combines Agile principles with Scrum practices. Scrum focuses on improving team interactions and enhancing responsiveness to change through short development cycles called "sprints." Each sprint typically lasts two to four weeks and includes all stages of the software development process from planning to testing.
Agile Scrum allows development teams to optimize their workflow, reducing risks and increasing customer satisfaction. Instead of detailed upfront planning for the entire project, Scrum encourages iterative and incremental planning, which is crucial in a rapidly changing technological environment.
Applying Agile Scrum brings several benefits:
-
Increased Flexibility: Scrum allows development to easily adapt to changing requirements, improving the final product quality. By breaking the project into short sprints, the team can change direction without having to overhaul the entire plan.
-
Improved Communication: Scrum encourages frequent communication among team members and with customers. Daily Standups and Sprint Retrospectives help better understand real needs and build stronger relationships.
-
Reduced Risk: Short sprints help identify and address issues early. The team can continuously receive feedback and adjust plans for subsequent sprints, minimizing risk and enhancing resilience.
-
Enhanced Customer Engagement (if applicable): Customers are regularly updated and can provide timely feedback through sprint review meetings. This ensures that the final product not only meets initial requirements but also aligns with evolving needs throughout the development process.
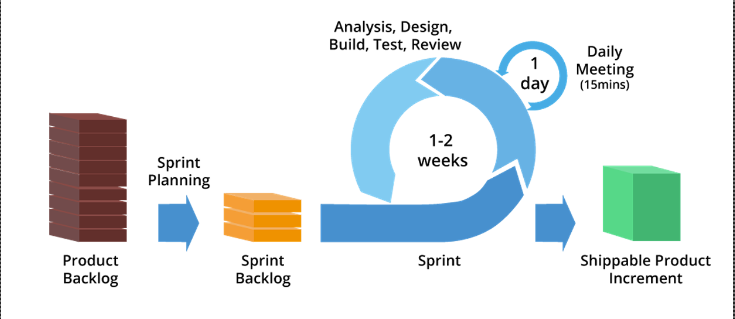
Project Development Process Based on Agile Scrum
-
Requirement Survey and Analysis: Identify user and system requirements through meetings, research, market surveys, and user feedback. Record requirements for features, performance, and security.
-
Product Planning: Create a list of requirements and features, prioritizing by value.
-
Sprint Planning: Plan for the sprint (usually 2-4 weeks), set goals, and select items from the Product Backlog to include in the Sprint Backlog.
-
System Design: Set up the structure for environment files (.env) and design the overall architecture, ensuring the system is scalable and maintainable.
-
Development: Install dependencies, deploy source code, and use Docker Compose to start necessary containers.
-
Daily Stand-up: Short daily meetings to update progress and discuss obstacles.
-
Testing: Use testing methods to test the API and user interface, validating that all endpoints work correctly and ensuring product quality.
-
Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team presents what has been completed and collects feedback.
-
Sprint Retrospective: Evaluate the workflow, identify areas for improvement for the next sprint.
-
Deployment: Configure Jenkins to automate the deployment process and ensure continuous deployment of the application.
-
Maintenance: After deployment, use Docker Compose to manage services, perform regular maintenance, and update based on user feedback.
By implementing these measures, the system will significantly improve its competitiveness and better meet the real-world needs of the e-commerce sector.